
History/origin: The kelvin is named after British physicist William Thomson, who was known as Lord Kelvin. This new definition results in a fundamental change in the kelvin, such that it is now dependent on the definitions of the second, the meter, and the kilogram. The definition of the kelvin was changed in 2019. It is also the unit of the Kelvin scale in which the null point (0 K) is the temperature at which all thermal motion ceases, known as absolute zero, or -273.15☌. It is defined as the energy equivalent of the triple point of water as given by Boltzmann's equation.
Celsius calculation free#
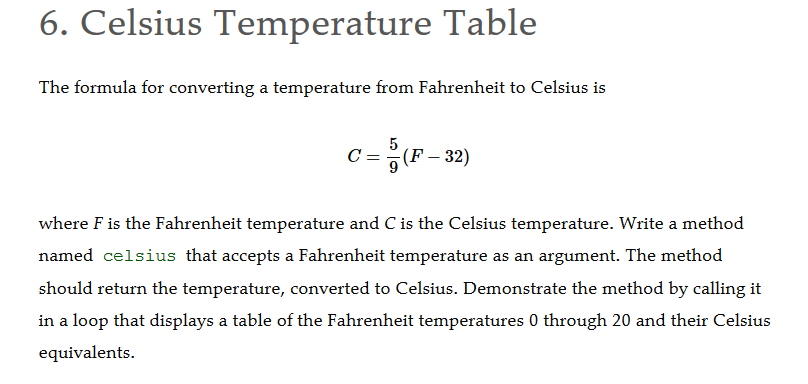
Feel free to contact us for any feedback.Definition: The kelvin (symbol: K) is the base unit of thermodynamic temperature in the International System of Units (SI). Lenntech BV is not responsible for programming or calculation errors on this sheet. The absolute zero point is by 0 K, this is -273.15 oC. This is the point where the molecules do not move anymore, so they do not give warmth. The temperature scale of Kelvin depends of the absolute zero point. The fundamental temperature scale is the one of Kelvin. Temperature is defined as the translation of heath between two objects. The kinetic energy changes when the temperature changes. Temperature is related with the kinetic energy of the molecules. On the Celsius-scale the boiling point of water with a pressure of 1 atmosphere is set at 99.975 oC. The triple point of water is defined at 0.01 oC.The Celsius scale is defined by the following two points:
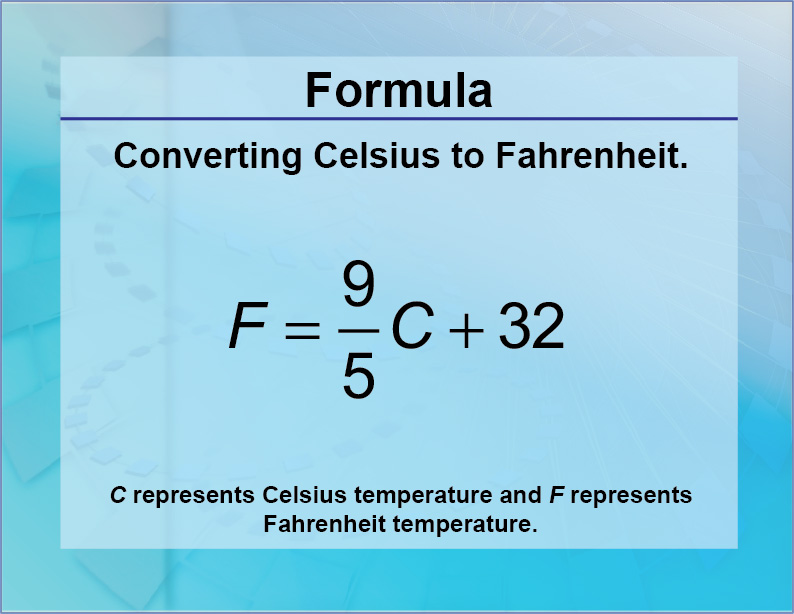
In 1948 the centidegrees (centigrade scale) were replaced by the degrees Celsius ( oC). This scale exists on 100 divisions, also known as centiscale. In the Celsius scale the freezing point of water is set at 0 degrees (centigrade) and the boiling point at 100 degrees (centigrade). Fahrenheit introduced his scale in 1724.Īnother scale is the Celsius scale. This means that between the freezing point and boiling point there are 180 divisions. The Fahrenheit scale is defined so that the melting point of water lays by 32 degrees Fahrenheit and the boiling point lays by 212 degrees Fahrenheit. The two most popular scales are the Celsius (made by Anders Celsius) and Fahrenheit (made by Gabriel Fahrenheit) scale. Between these two temperatures a scale is made. Present temperature scales have two basic points: from when the water starts to freeze and when it starts to boil. Mercury also stays in the liquid phase for a great range of temperature. The reason that mercury was used is that the thermal expansion of mercury is large, mostly homogeneous and it does not stick on the glass. In 1724 Gabriel Fahrenheit introduced the medium mercury in the thermo scopes. In 1610 Galileo introduced wine in the thermo scopes instead of air. The earlier measurement instruments for temperature where called thermo scopes. He had a scale of 4 degrees warmth and 4 degrees of cold. One of the first who wanted to make a temperature scale was Galen (ca. The idea of measuring temperature exists a long time. This means that liquid, solid and gas phase from a matter appear at the same time. The triple point is a theoretical point where the three phases of a matter (for example water) come together. One degree Celsius equals the change of temperature with one degree on the ideal gas-scale.The triple point of water is defined as 0.01 oC.The Celsius-scale is defined by the follow two points: The triple point of water is 273.16 K, which is 0.01 oC (degrees Celsius). In the 13th CGPM in 1967 was decided that the unit of temperature will be the Kelvin, and not 'degrees Kelvin'. The Kelvin, unit of thermodynamic temperature, is the fraction 1/273.16 of the thermodynamic temperature of the triple point of water (13de CGPM (1967), Rés. The tendency of a substance or an object to transfer heat to its surroundings.ĭefinition of the thermodynamic temperature: With this program, the units of temperature (degrees Celsius, Kelvin and degrees Fahrenheit) can be converted.Ĭalculate the wind chill Definition of temperature:



 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
